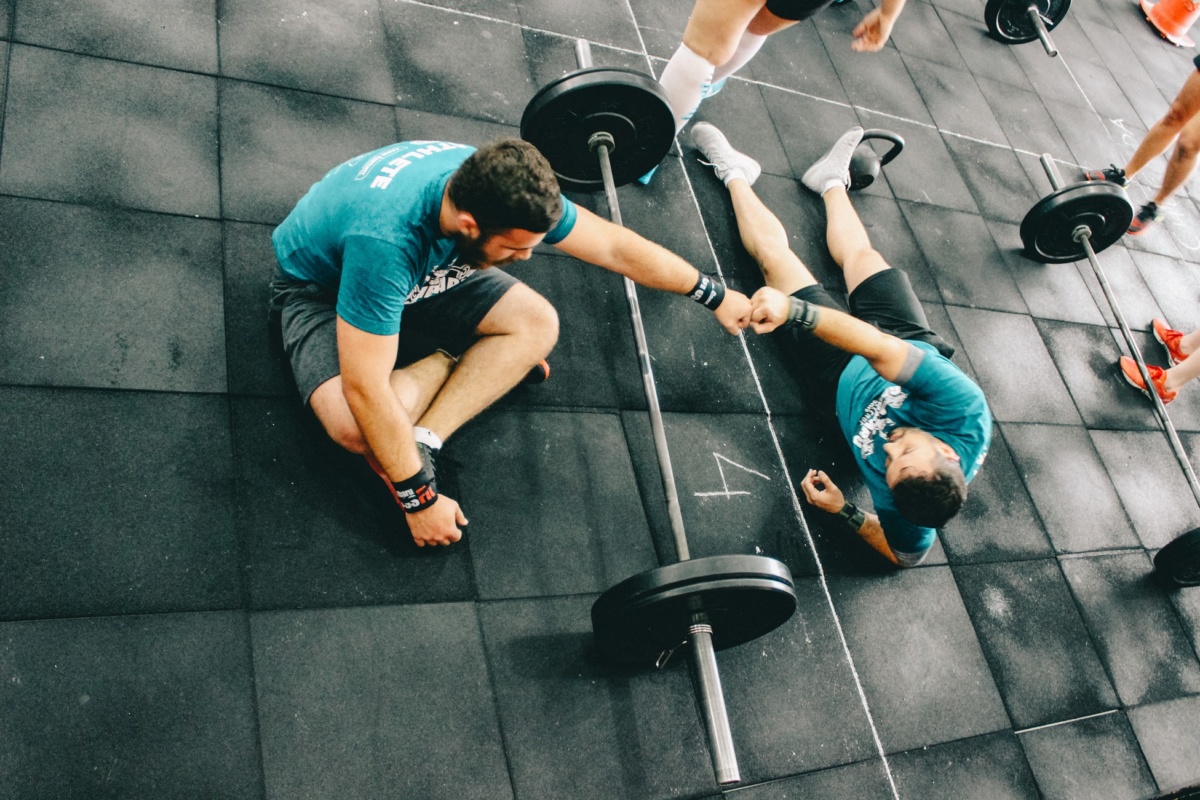
The source of energy during physical activities.
When engaging in physical activities, various substances in your body are utilized to support muscle movement and development. While carbohydrates are usually the primary focus, glycogen plays a crucial role in this process.
Glycogen represents the stored form of glucose in your body, stored within the muscles and liver. During physical exertion, blood circulates to provide energy to your muscles. However, the issue lies in the fact that blood is not actively extracting glucose from your intestines, leading to an energy deficit. Fortunately, most bodies can store up to a pound of glycogen within the muscles, which can be utilized for glucose when necessary. Intense exercise depletes more of this glycogen, resulting in quicker exhaustion. This is why endurance-focused athletes load up on carbohydrates; during sustained activity, the body’s demand for carbohydrates surpasses that of glycogen.
To endure high-intensity exercise, it is essential to boost your glycogen reserves. How can this be achieved? By enduring through exercises that burn carbohydrates without affecting glycogen levels, helping your muscles become more efficient in utilizing glycogen. By doing so, your body will retain more glycogen when pushing your limits, delaying its depletion. Carb-loading before exercising allows you to maximize your glycogen stores efficiently.